Air Filters
Introduction
This article takes an in depth look at air filters.
Read further to learn more about topics such as:
What is an air filter?
Types of air filter media
Performance of air filters
Types of air filters
And much more...
Chapter 4: Types of Air Filters
The types of air filter equipment are as follows:
HEPA Filters
HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air filter. According to MIL-STD-282, to be considered an authentic HEPA filter, the filter must capture at least 99.97% of particulates in the air measuring 0.3 µ in diameter and larger. A 0.3 µ particle is considered to be the most difficult particle size to capture. In European and ISO standards, which are ISO29463 and EN 1822, the required efficiency is 99.95%.Air filters with efficiency between 85% and 99.95% are considered to be EPA filters.
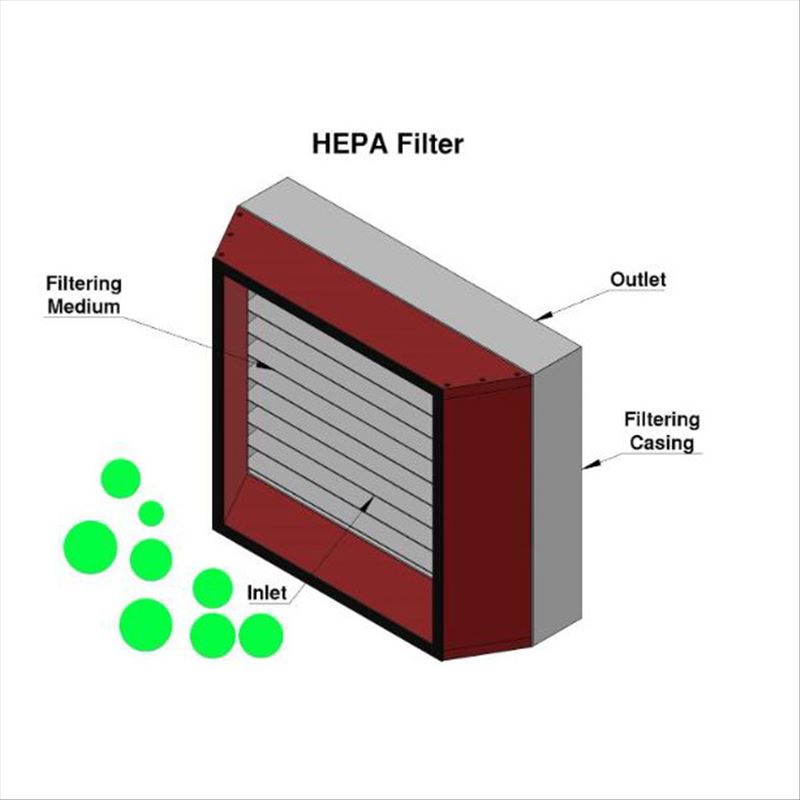
The filter media for HEPA filters are commonly made from several layers of borosilicate glass fibers or polypropylene fibers randomly arranged like a web to maximize particulate arrestance. HEPA filters rely on the combination of these mechanisms to capture the particulates:
1.Impaction Impaction happens at the surface of the filter media to sieve the particles larger than the mesh openings of the filter media. These particles crash into the fibers and are directly captured. This mechanism usually works for particles larger than 1 micron.
2.Interception Particles that are not sieved at the surface of the filter medium move to a depth of the filter media. However, these particles collide between the fibers and are removed from the airflow.
3.Diffusion Very small particles collide with the gas molecules; this causes them to move erratically within the filter medium and eventually strike and stick to the fibers. This phenomenon is called Brownian motion. For particles with sizes near the MPPS, interception and diffusion are the two most important filtration mechanisms.

HEPA filters protect the health of the users as they can effectively capture disease-causing microorganisms, allergens, odors, irritants, and smoke. They are widely used in hospitals, clinics, cleanroom environments, and chemical production facilities.
ULPA Filters
Ultra-low particulate air (ULPA) filters can remove even smaller particles in the air, down to 0.12 µ in diameter with at least 99.9995% efficiency. ULPA and HEPA filters have the same working mechanism; however, ULPA filters have lower filter medium porosity. Hence, their greater filter media density reduces airflow; this results in higher energy consumption than HEPA filters. Moreover, they have a shorter service life and are more expensive.
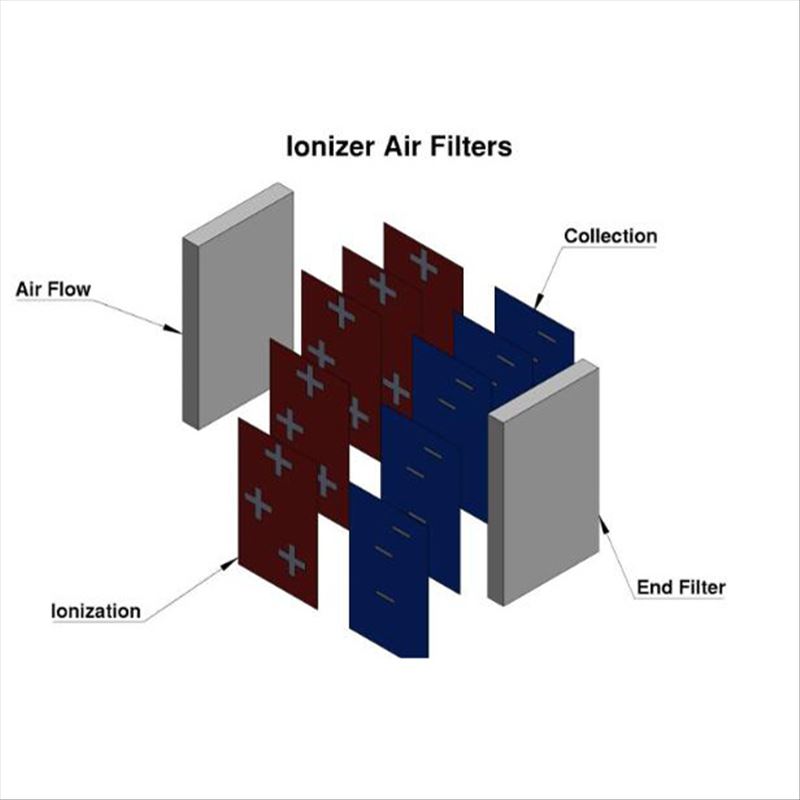
Ionizer Air Filters
In an ionizer air filter, the unclean air first passes through a pre-filter, then through an ionizer to give the airborne particles an electrical charge. The electrically charged particles are then attracted to and retained on the oppositely charged plates. The filtering mechanism does not involve filter media. Ionizer air filters are commonly referred to as electrostatic air filters.
Ionizer air filters have a MERV rating ranging from 4-5. They are cost-effective, have a long service life, and must be maintained regularly to maximize airflow. However, they are not the best choice for users with respiratory problems. The electric field created can produce ozone molecules that can worsen asthma and lung diseases.
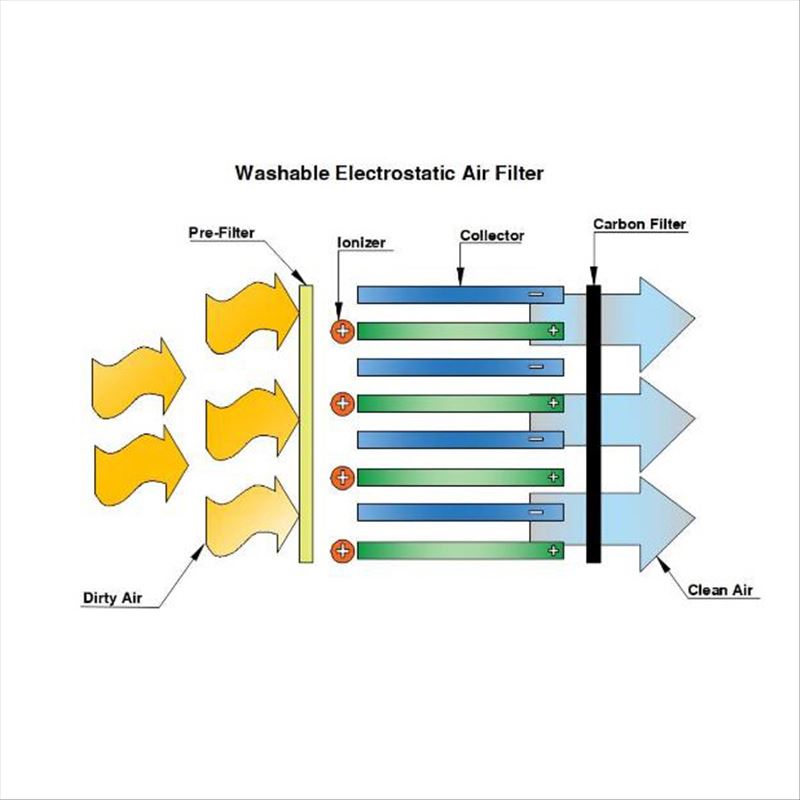
Washable Electrostatic Air Filters
Washable electrostatic air filters rely on an electrostatic filter media, which is typically made from woven polypropylene or polyester. Airborne particles encounter friction as it passes through the filter media. They eventually become charged and are attracted to the inner layers of the filter media. The filter media holds the particles by static electricity until it is washed to remove those particles. Its electrostatic property remains constant over time and is not affected by washing.
Washable electrostatic air filters have a MERV rating ranging from 6-8. They are safe since they do not produce ozone. They are inexpensive, durable, and have a long service life.
Activated Carbon Air Filters
Activated carbon air filters are effective at removing gaseous pollutants, fumes, vapors, and odors present in the air. The gaseous molecules in the air are absorbed and retained in the outer surface of the carbon atom. However, to effectively remove those molecules,they must be allowed to settle in the activated carbon matrix for a certain amount of time.
When used as a stand-alone filter, they cannot capture solid particulates. Hence, they are typically used in conjunction with HEPA and electrostatic air filters to improve air quality. The required replacement frequency of the activated carbon filter media is unknown since it shows no signs of saturation.

Ultraviolet Air Filters
Ultraviolet (UV) air filters use a special light that is installed inside the air flow stream before or after an air flow unit to ensure that the air circulation passes through the filtration system. As air passes through the filter, a focused UV light shines into the air flow sterilizing the air and removing microbes, viruses, bacteria, and mold spores.
A combination of regular filters and UV filters cleans physical particles and viruses. UV filters use electromagnetic waves that do not bond with air molecules. They are very low maintenance and only need to be replaced once a year. UV filters are highly efficient and clean constantly without producing any noise. Unlike traditional filters, UV filters do not accumulate dirt, dust, or particles that block other filters.
UV air filters are unable to remove solid particulates and gaseous pollutants when used as a stand-alone filter. When they are combined with HEPA filters, the combination produces significant improvement in air quality. Some forms of UV filters are rated for removing the COVID virus.

HVAC Filters
HVAC filters prevent particulates (e.g., dust, dirt, debris) and other contaminants in the air from entering the internal components of the HVAC system. These solid particles can damage and deteriorate the efficiency of the HVAC system. HVAC filters also improve the circulating air quality inside a room or facility. AC filters and furnace filters are types of HVAC filters and basically have the same design and construction.
Since the operation of HVAC filters is based on airflow, it is recommended you use furnace filters with a MERV rating lower than 13 if they will be installed in residential spaces.

Engine Air Filters
Engine air filters are rectangular pleated filters that remove particulates from the air before it flows to the engine of a vehicle. Accumulation of solid particles inside the engine can cause wear and damage to the engine's internal components, increased fuel consumption, and deterioration of its efficiency.
Engine air filters should be replaced between 15,000 and 30,000 miles depending on the type of vehicle and driving conditions. Accumulation of solids in the filter restricts the airflow, limits acceleration, and causes the vehicle to emit toxic gases.

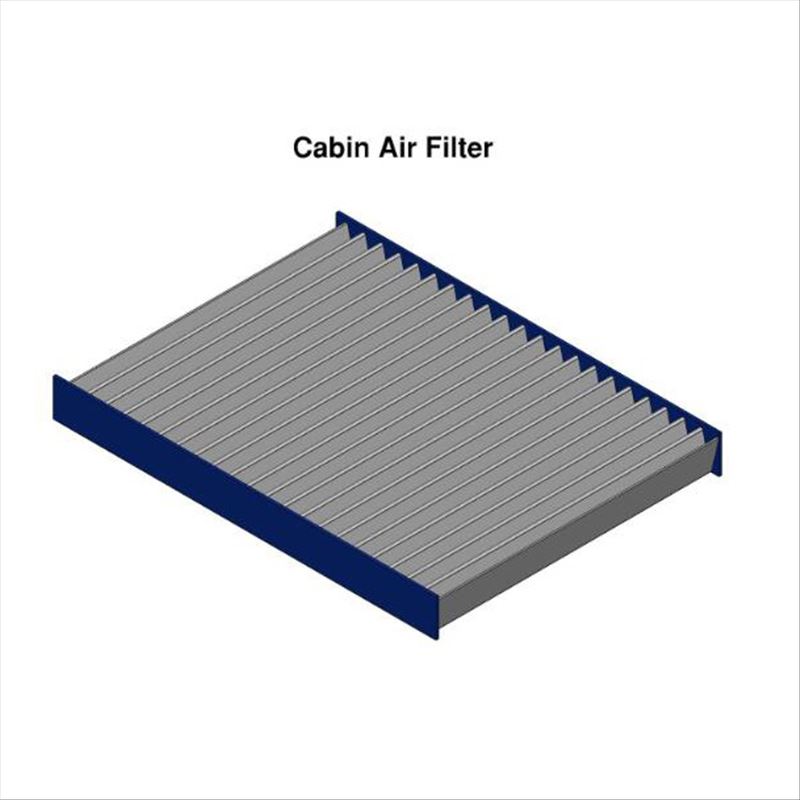
Cabin Air Filters
Cabin air filters are HVAC filters designed for vehicles. They are usually made from multi-layered paper filter media. They provide clean air to the passengers and protect the air conditioning system of the vehicle. They filter particulates in the air drawn from the passenger compartment before it enters the vehicle's air conditioner. Cabin filters have different replacement frequencies than engine air filters.

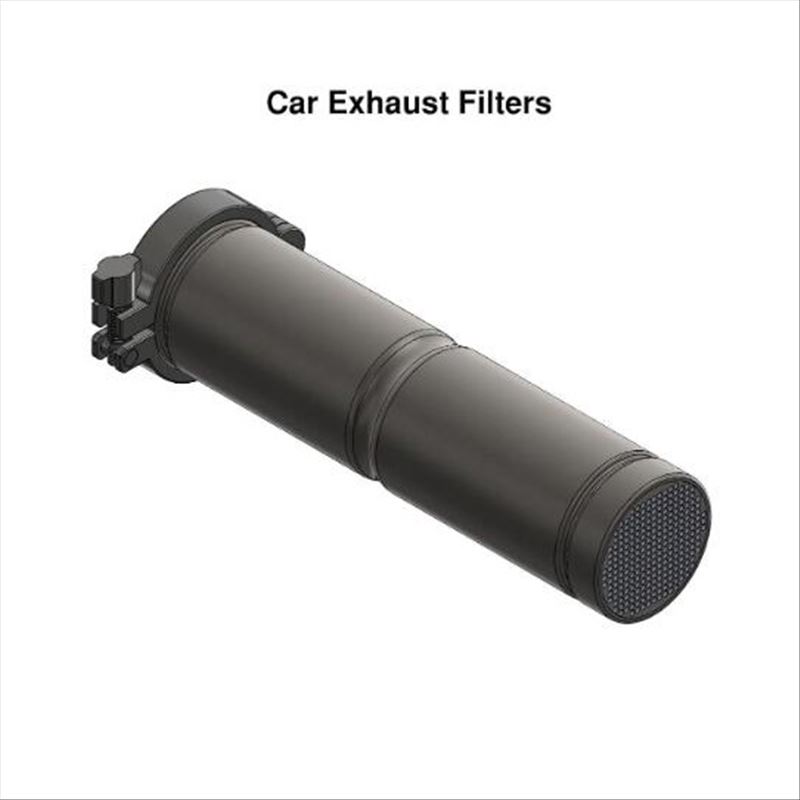
Car Exhaust Filters
Car exhaust filters are directly installed in the exhaust pipes of vehicles. They capture fine, harmful particles from engine emissions to prevent them from polluting the atmosphere. However, they are unable to capture toxic gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide.

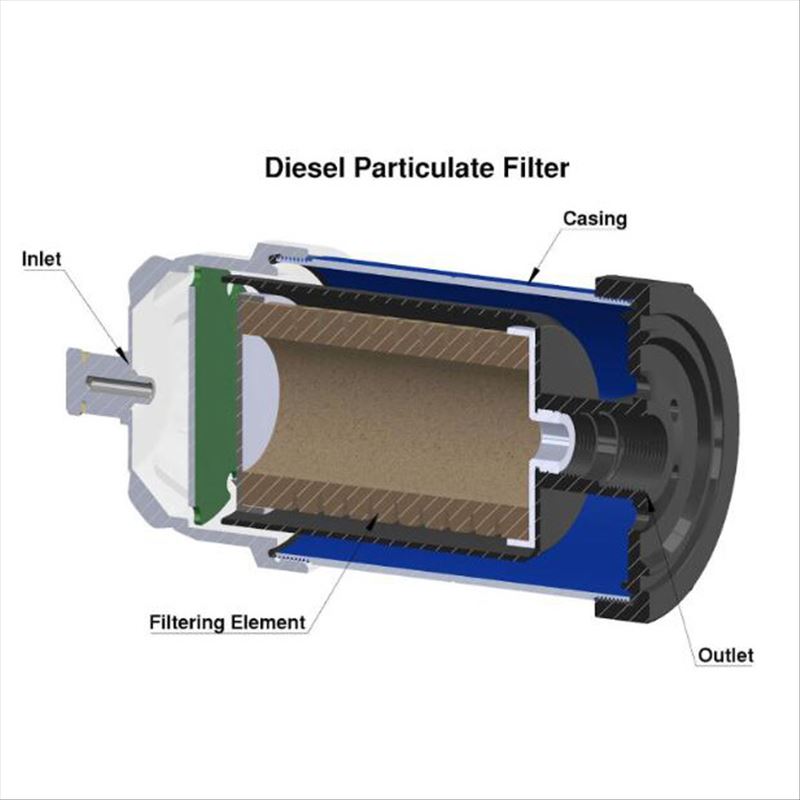
Diesel Particulate Filters
A Diesel particulate filter (DPF) is a special type of car exhaust filter designed for diesel-powered engines. Their filter media are made from a ceramic material formed into a honeycomb structure. The filter media collects soot, ash, and other particulates.
DPFs have an oxidative catalytic converter that converts the carbon content of the accumulated soot into carbon dioxide by passive or active regeneration. Passive and active regeneration can take place automatically without the initiation of the driver. This makes DPFs a self-cleaning filter;however, regular maintenance is still necessary.
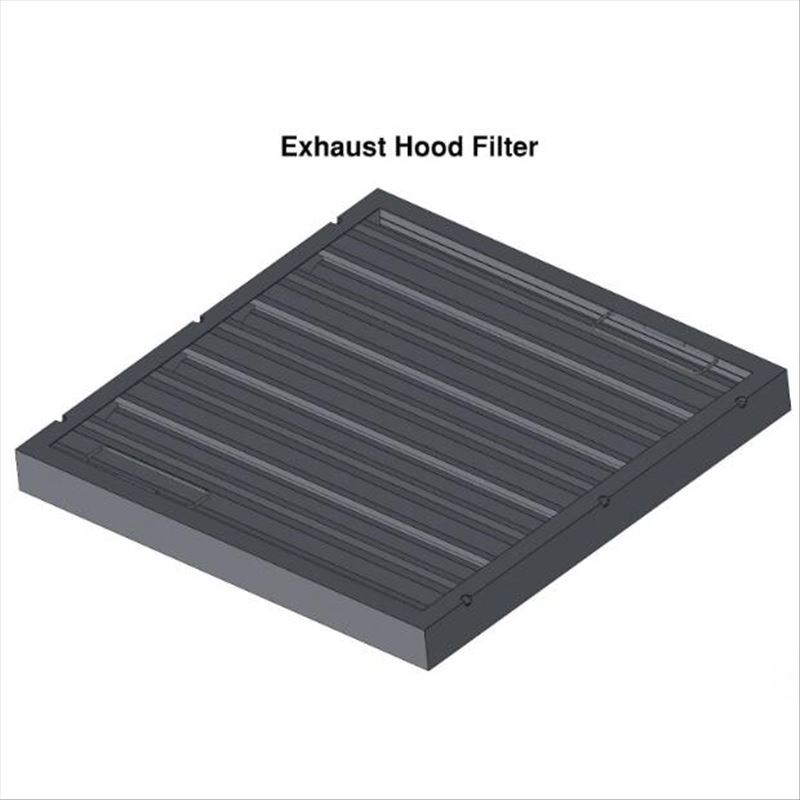
Exhaust Hood Filters
Exhaust hood filters, or grease filters, are installed in kitchen hoods in order to remove grease, oil, smoke, and odors in the air produced during cooking.They are usually made from metal filter media.They are installed on top of stoves, grills,and fryers.

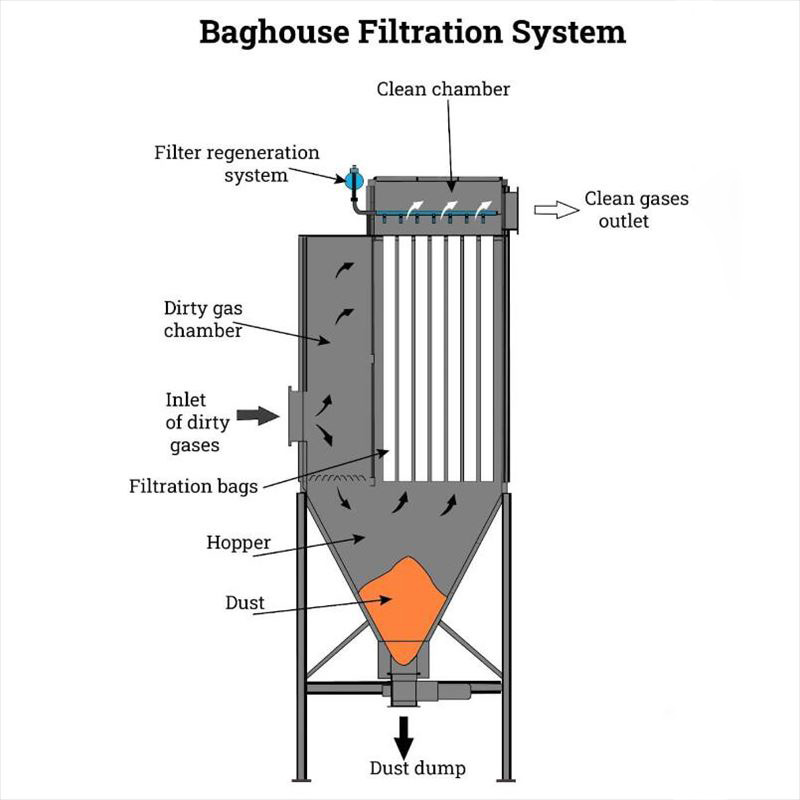
Baghouse Filters
Baghouse filters remove dust particulate and air pollutants from dirty air streams created by manufacturing and processing equipment. Any industry where nuisance dust is created needs a dust collection system. Typical industries are wood processing, food manufacturing, and metalworking.
A baghouse filtering system contains filter bags, filter cartridges, or pleated filter elements. Filter Cartridges are made of polyester and paper media treated with coatings like PTFE and Nanofiber, while filter bags are made from polyester felts and treated cotton materials.
The disposable filters of a baghouse system capture dust particles from the air that passes through them. Clean air exits the baghouse either venting outside or is recirculated through the environment. Excess dust released from the filters falls into a hopper below the baghouse housing.Baghouse filters have a large airflow capacity and are designed for industrial applications and use.
Exhaust Filters
Exhaust filters are installed in ventilation systems to filter the air from a closed space before releasing it to the environment.
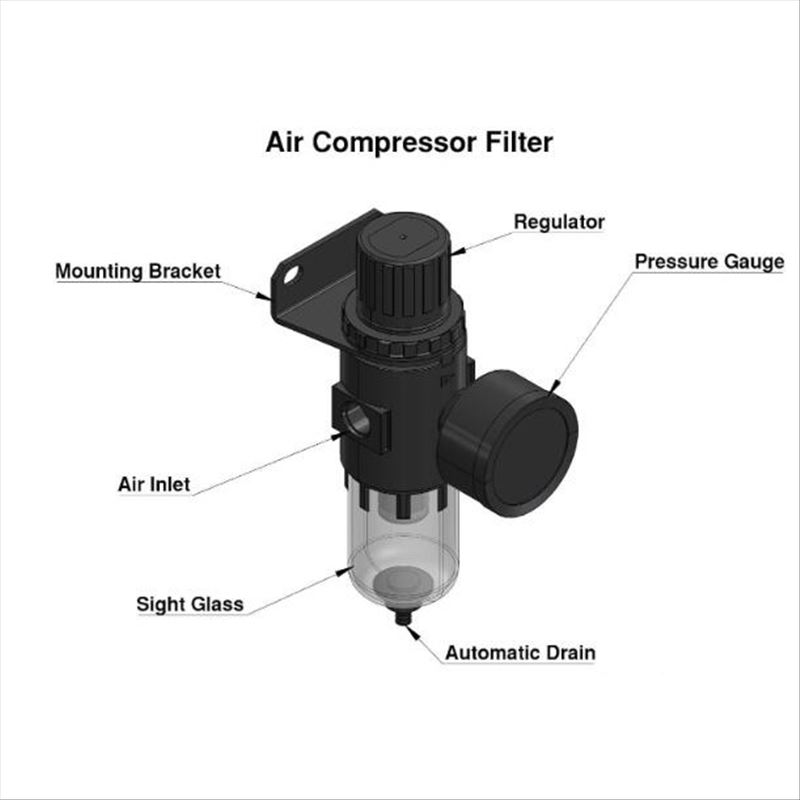
Air Compressor Filter
Air compressor filters, or airline filters, are installed in condensed airlines, which are used to remove water, solid particulates, oil, and other contaminants in a multi-stage filtration process. They prevent these contaminants and protect the internal components of the air compressor unit, ensuring the unit is in top condition.

Summary
1.Air filters are devices used to remove airborne particles and pollutants that are hazardous to health and the ecosystem. These devices utilize a filter media, which captures those particles on its upstream side.
2.Pleated air filters have folds or pleats, which increase their surface area. Non-pleated air filters provide maximum airflow and are suitable for higher airflow pressures.
3.Air filter media can be made from paper, foam, carbon, aluminum, steel, fiberglass, or plastic.
The performance of air filters is reported by the MERV rating, arrestance, dust holding capacity, dust spot efficiency, and MPPS. The MERV rating is commonly used; it refers to the air filter's efficacy in removing particles with sizes between 0.3 and 10 microns.
4.HEPA filters capture at least 99.97% of particulates in the air measuring 0.3 microns in diameter. In ISO and European standards, the efficiency must be at least 99.95%.
5.Impaction, interception, and diffusion are the filtration mechanisms that occur in HEPA filters.
6.ULPA filters remove particles of up to 0.12 microns in diameter for at least 99.99% efficiency. Their filter media density is higher than HEPA filters; hence, airflow is more restricted.
7.Ionizer air filters and washable electrostatic air filters attract particulates by static electricity.
8.Activated carbon filters and UV air filters remove toxic gases and microorganisms in the air respectively.
9.HVAC air filters protect the critical components of the HVAC unit and purify the air for the users. The types of HVAC air filters are AC filters and furnace filters.
10.Air filters used in vehicles are the engine air filters, cabin air filters, car exhaust filters, and diesel particulate filters (DPF).
Baghouse filters are pollution control equipment that removes particulates and pollutants in flue gases from process equipment before releasing them into the atmosphere.
11.Exhaust hood filters and exhaust filters are used in commercial and residential ventilation systems.






















